SHARE
Commercials
More Posts
Dec 12, 2024
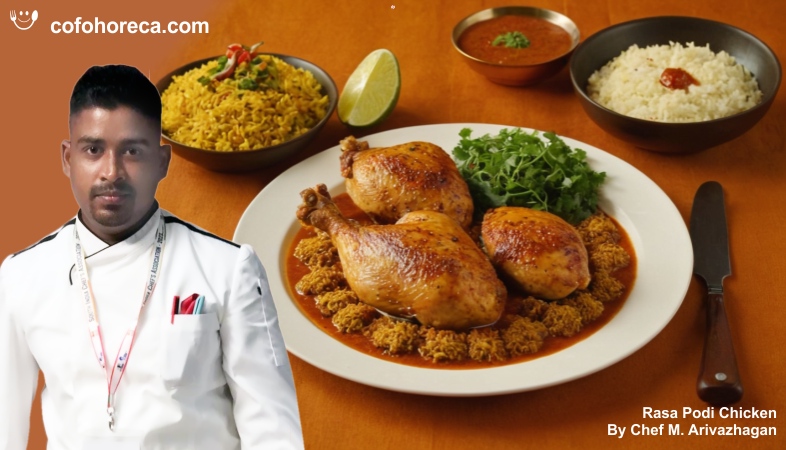
Rasa Podi Chicken - By Chef M. Arivazhagan
Feb 19, 2025
Dhokla Chicken Tikka Sandwich - By Chef Hardev Singh
Dec 12, 2024
Rasa Podi Chicken - By Chef M. Arivazhagan
Feb 19, 2025
.png)